
Animal identification tags are important for both legal and health & safety reasons where animal by-products are sold into the human food chain. The tags on dairy cattle are used to record data and trace the animals throughout the milk production process. The tags themselves, attached through the livestock’s ear, comprise of two flexible plastic leaves and a tamper-proof pin fastener. They must remain on the animal – and complete in themselves – when subjected to all expected in-service forces. Specific standards require testing for both tensile strength (by means of a transverse pull test) and pull-off/pull-out forces along the axis of the pin. The software–contolled test stand is able to hold the tags at a target load and then pull further at contolled speed (typically 500 mm/min) until breakage. Once failure occurs, the tags must be unusable as part of the traceability requirements. The transverse pull test can be performed with suitably rated tension wedge grips. The pull-out test on the pin can be achieved with custom grips designed to pull axially and support the leaf surfaces.
Mecmesin Systems: MultiTest console-controlled force test system, 5 kN wedge grips
Case Study: Animal Identification Tags
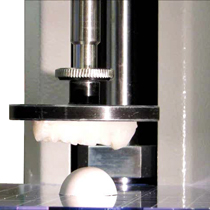
Scientific research in the sphere of physiology, anatomy and medicine has far-reaching impact on the health and well-being of humankind. The methodical application of testing and investigation into how biological systems behave and react to change allows the furtherment of medical science. The discipline of dentistry can employ mechanical testing to evaluate the bite strength of the mandible/maxilla system throughout the aging and wearing process, by repeatable compressive strength tests. One specific example uses a computer-controlled test stand to compress a plaster of Paris dome-shaped sample (which has comparable mechanical properties to hard, brittle food items, like nuts) to measure ultimate bite strength. Dental model attachments to the compression plate represent the tooth profile within the jaw and in addition to the force measurement, further evaluation of the fractured sample – size and number of fragments - also influence the scientific appraisal of mechanical performance. As the teeth wear, the profile changes and the effectiveness over time of the ability to fracture the foodstuff can be determined. The test program records the peak force at fracture and uses stop-at-break functionality to avoid damage and reset, then the output data is further analysed in Excel® - allowing the flexibility to continue research out in the field, by use of portable computers. The Emperor™ software’s ability record all of the data is invaluable in the thorough understanding necessary in a scientific project. Furthermore, this ethical engineering solution negates the need to experiment with living primate specimens.
Mecmesin Systems: MultiTest computer-controlled force test system, compression plate accessory

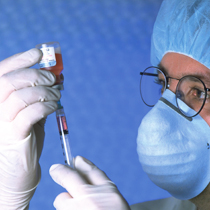
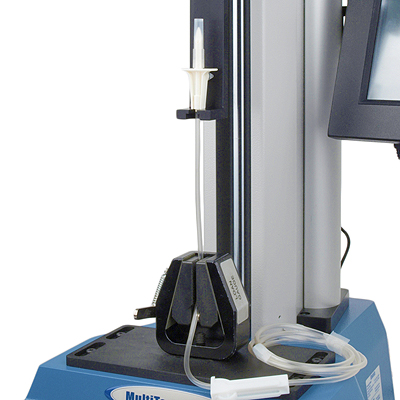
Medical device manufacturers operate in one of the world’s most competitive and highly-regulated industries, where success and lives hinge on compliance to standards, time-to-market and results traceability (raw data retention). A robust audit trail is important for the OEM if the customer has a product problem in the future. Syringes must deliver and extract fluids in a smooth, controlled manner; a plunger that is too easy or hard to actuate, or that stalls or judders on depression will not perform reliably during injection or aspiration. The testing of manually operated sterile single-use hypodermic syringes for glide (in both aspiration and expression strokes) force is essential under industry standards. These forces will be determined by a range of variables, the size of the syringe/needle aperture, the ‘fit’ of the plunger within the syringe barrel, the materials used and, in service, the density of the tissue substrate and the viscosity of the liquid. The syringe must be developed with the optimum balance of these variables to assure consistency and usability. Typically, a constant rate of plunger depression (and withdrawal) of the order of 100 mm/min is indicated for this test. A compression tester should be employed that deals with security – a log on for operator identification - and software to accurately control the plunger displacement and record the data. A fixture to grasp the finger flange for tension and compression strokes, with adjustability for syringe sizes, may also be required.
Mecmesin Systems: Touch screen test systems, Emperor™ (Force)
Video: Syringe plunger actuation force
Standard: ISO 7886-1

The 6% conical taper Luer connector for syringes, needles and other medical devices can be push/pull taper only, or a taper and screw (“Luer lock”) fitting. Light assembly and disassembly torque to turn is required to seal so that even a child could use successfully, whilst remaining leak-proof. However, a successful seal at low torque improves at higher torque. In the case of Luer locks, torque assessment should be performed on a low-level torque testing system, with a motorized base plate and a low capacity (e.g. 1.5 Nm) torque transducer. The most common test involves tightening the Luer lock connection between a needle housing and a fluid-filled syringe to a pre-determined torque, and visually inspecting the joint for leakage. Universal gripping pegs may be used to hold the sample in place, although customized fixtures ensure greater accuracy and repeatability – keeping the sample concentric with the torque axis is an important consideration. A floating fixture, or similar, to allow secure location into the needle attachment component should also be employed. For in-house quality standards compliance, a semi-automated syringe tester using a touch-screen controlled torque testing system which can be programmed with acceptable limits for the syringe is recommended. The operator is presented with a colour coded pass/fail result for easy identification of the sample status.
Mecmesin Systems: Touch screen torque test systems, Emperor™ (Torque)
Video: Semi-automated syringe tester
White Paper: An Examination Of Needle And Syringe Force Testing

The foil lid of blister packaging must allow separation in normal use by means of peeling the flexible layer from the formed container without tearing. The adhesive strength of the bond should facilitate this ease of opening and also guarantee the reliable sealing of the product within, which may be a liquid or gel with hygiene or sterility requirements in the pharmaceutical or food industries. Peel testing of these packages to external or internal standards has several challenges in order to replicate the actual manner in which the elements are separated in service and to repeatably focus the test of the adhesive characteristics of the bond itself. Maintaining the peel angle (initiated at 135 degrees) to within the desired specification may require the design of a custom fixture – a jointed chain can effectively replicate the manner in which a consumer will apply the tension to the lid. Grasping of the corner of the foil in a manner akin to human fingers will require suitably sized pinch grips. In order to focus the test on the bonding around the blister perimeter, the surface needs to be kept flat and in a non-deformed condition, to avoid introducing inaccuracies into the process and ensure repeatability. The use of a pneumatically-activated vacuum fixture specifically moulded to the blister profile is the reliable solution.
Mecmesin Systems: Touch screen force test systems, pinch grip
The 6% taper Luer lock-type of fitting (screw or lug) for syringes, needles and other medical devices has the primary purpose of ensuring a leak-free connection in delivering fluids. For systems using semi-rigid materials (e.g. plastics), the relevant standards require a specific metal conical reference fitting to be used, either male or female, to test both parts of the connector, ensuring control over dimensions and tolerances. A test system which is able to accurately apply a top-load axial force is required (27.5 N), with the simultaneous application of a very small torque value of 0.12 N.m. There are additional considerations in the design of an automated, purpose-built, test system for these standards, which are validating that the fastening torque is satisfactory to achieve the seal. Namely, the provision to supply the fluid to the Luer component and to a stipulated pressure for the liquid leakage standard, or to draw fluid into a syringe to a percentage of its capacity for the air leakage during aspiration (filling) test. The testing for liquid leakage requires the application of an effective internal water pressure of between 300 kPa and 330 kPa once assembled to the reference fitting. Visible inspection for leakage is then performed – falling drop of liquid or continued formation of air bubbles.
Mecmesin Systems: Helixa precision torque test systems, Mecmesin purpose-built test systems
Applicable Standards: ISO 594-2, BS EN 1707, BS EN 20594-1 ISO 80369
White Paper: An Examination Of Needle And Syringe Force Testing

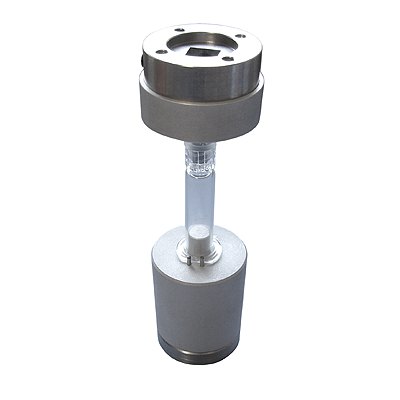
The 6% (Luer) lock-type of conical tapered connector, used in fluid delivery systems in the medical field, must ensure leak-free performance at all times. Whether in hand-held syringes or other devices, such as infusion pumps supplying nutrients or medication, the seal must remain intact so as to provide the exact dosage – and this unscrewing torque test evaluates the device’s resistance to coming apart. The testing standard for semi-rigid versions of Luer components requires precise assembly of the connector under inspection (male or female) to a metal reference fitting prior to performing the specific functional test - 27.5 N top-load and 0.12 N.m torque. Due to the light loading values required for these devices, a precision test stand is needed. The unscrewing torque test requires that a very small torque (0.02 +0/-0.002 N.m) is applied and then held for a minimum amount of time. Precise alignment is essential to ensure than no other forces occur along any other axis, and the test stand must be able to provide this level of control. The Luer connector must remain attached to the reference fitting to comply.
Mecmesin Systems: Helixa precision torque test systems
Applicable Standards: ISO 594-2, BS EN 1707, BS EN 20594-1 ISO 80369
White Paper: An Examination Of Needle And Syringe Force Testing

Medical device connectors with a Luer lock (6% taper), which are manufactured from semi-rigid materials, are subject to an ease of assembly test under industry standards, which stipulates precise application force and torque values. Rigid devices need only be assembled to the definition of “secure”. To assemble the Luer lock to the metal reference fitting (27.5 N top-load and 0.12 N.m torque), connectors made of plastic require a test stand which is then capable of simultaneously imparting an axial force, not exceeding 20N, on the screw fitting together with a small torque, not exceeding 0.08 N.m. The connector should completely assemble under these loads to pass this specific fastening torque test.
Mecmesin Systems: Helixa precision torque test systems, Mecmesin purpose-built test systems
Applicable Standards: ISO 594-2, BS EN 1707, BS EN 20594-1 ISO 80369
White Paper: An Examination Of Needle And Syringe Force Testing

Connector components of a fluid delivery system must be able to be assembled quickly and reliably in the medical and healthcare environment. The Luer lock solution is threaded (or has a lug) and more secure than the Luer slip-type and so must be able to be easily screwed together to provide a leak-free seal, that will not be compromised by under or over tightening – and verified by fastening torque testing. The relevant standard refers to the latter condition as overriding, and repeatable testing to this standard requires the precise application of a 0.15 N.m torque to the component in the tightening direction. This torque must be held constant for 5 seconds and the test stand program must be able to facilitate this condition. As with the related Luer lock tests, the sample must first be assembled to the reference fitting by a simultaneous maximum axial force of 27.5 N and a light maximum torque of 0.12 N.m torque prior to the overriding torque application
Mecmesin Systems: Helixa precision torque test systems
Applicable Standards: ISO 594-2, BS EN 1707, BS EN 20594-1 ISO 80369
White Paper: An Examination Of Needle And Syringe Force Testing
The performance of Luer locks (6% conical taper connectors with a screw thread or lug method of assembly) must be maintained throughout the duration of their use in the fluid delivery system. These medical devices are designed to ensure a leak-free condition, whilst being quick and easy to remove and replace as demanded by the patient’s treatment program. In addition to tests focusing on the assembly of the connector, industry standards also prescribe tests to meet durability demands while connected at a reference fastening torque. This particular requirement needs a test stand capable of applying both a torque (0.12 N.m) and an axial force (27.5 N) held for 5 seconds, to assemble the Luer lock initially. To complete the stressing of the components, a constant temperature of 20 ± 5 °C (27 ± 5 °C in tropical climates) is maintained for a period of 48 ± 1 h. The components should be free from cracking at the completion of the test. Additional consideration should be given for specific environmental conditions applicable to the device’s use – which may include contact with chemicals in addition to elevated temperatures.
Mecmesin Systems: Helixa precision torque test systems
Applicable Standards: ISO 594-2, BS EN 1707, BS EN 20594-1 ISO 80369
White Paper: An Examination Of Needle And Syringe Force Testing

The 6% taper Luer lock-type of connector has widespread use for hypodermic syringes, needles and with certain other apparatus for medical implementations, such as transfusion equipment, for the delivery of fluids. For systems using semi-rigid materials (e.g. plastics), the relevant standards require a specific metal reference conical fitting to be used, either male or female, to test both parts of the connector. The testing of separation (pull-off) compliance requires that the element of the connector under test remains attached to the reference fitting. The Luer component is first applied to the reference fitting by a maximum axial force in conjunction with a precise, small value, maximum torque (27.5 N top-load and 0.12 N.m torque). Once located, the test must apply another strictly axial force away from the test fixture at a constant rate of 10 N/s up to a maximum value of 35 N and for a minimum time of 10 s, in order to evaluate the pass or fail condition for the pull-off test. The subsequent part of the method may require a different test stand to complete the full quality assurance process to acceptable accuracy, due to the significantly different force values to that required to locate the fitting initially. A constant rate of traverse system can achieve the necessary force application rate by prior testing to equate the displacement rate for the sample type under inspection.
Mecmesin Systems: Helixa precision torque test systems and MultiTest motorised test system
Applicable Standards: ISO 594-2, BS EN 1707, BS EN 20594-1 ISO 80369
White Paper: An Examination Of Needle And Syringe Force Testing

The components in rotating machine tools which are designed to work on materials, need to remain securely located in order to accurately wear the target surface. Small abrasive disks used in the dental industry (to shape implants), should be tested for integrity by evaluating their resistance to an applied torque to turn created between the implant surface and the driving spindle of the tool. Using a custom-designed adaptor, the abrasive disks may be tested to check that they do not become loose on their central hub when in service. Should the breakaway torque be less than required standards, the supplied batch can be rejected. The disks are marked clearly prior to being loaded onto the adaptor to show any subsequent rotation. The adaptor securely clamps the abrasion surface itself and a custom probe is lowered into the spindle bore. The software program rotates the locked probe 90 degrees clockwise and 180 degrees anti-clockwise. If the disk has rotated in the hub, then the component fails. Slippage around the spindle or rotation against the fixing (much less likely) would show no indicated disk rotation. The torque is measured and the test results graphically displayed to further quantify the level of discrepancy between specification and achieved peak torque.
Mecmesin Systems: Vortex torque test systems, EmperorTM (Torque)
Video: Dental abrasive disk testing
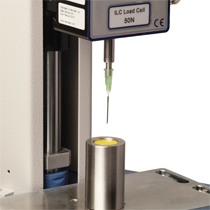
The medical devices and associated services industries are subject to strict quality standards testing. The complete life-cycle of the equipment is covered, including the safe disposal of used, contaminated items. Manufacturers of products involved with the safe discarding of medical devices with needles (‘sharps’) must conform to British Standards to provide proof against puncture by clinical waste materials. These sharps bins will be handled by staff from several organisations in the chain, not all specifically trained in medical practices, thus safety must be assured against the puncture of the container material by the waste. A puncture resistance testing process should allow a variety of sample types – specifically material thickness – to be securely located by means of an adjustable base fixture that has sufficient clearance to drive the needle point a certain distance through the surface of the standard diameter sample. An extension rod to fit the syringe hub is required for the crosshead fixture. Measurement of the peak force applied to create a breach can be achieved with computer controlled test programming and run from a touch screen console with each unique test associated with a sample type.
Mecmesin Systems: MultiTest touch-screen test system

All sterile medical devices require validation of their packaging. The flexible sterile barrier must be shown to be effective throughout the product's claimed shelf-life. The integrity of seals and welds is of critical importance and the testing of the bonding strength of these seals is often performed by peel test, the flexible material on both layers necessitating either 180 degree or T-peel. These tests are also relevant to package openability and evaluating the manufacturing processes’ ability to produce consistent seals and the peak force and/or the average force to open the seal may be relevant. Inspection after the test may reveal either the adhesive has failed to adhere to a substrate (adhesive failure), in which case the bond strength has been measured. Conversely if the bond has failed internally (cohesive failure), or the packaging material has delaminated, torn or failed in another manner, then the test has exposed deficiency in the overall specification of the seal. Usually a representative strip is cut across the seal of a standard width and a T-peel is performed. An important consideration in the fixture design may be to mitigate against bending – by supporting the unpeeled portion of the sample at 90 degrees to the peel direction.
Mecmesin Systems: MultiTest console-controlled force test system, lightweight double-action vice grips
Standards: ASTM F-88, EN 868-5
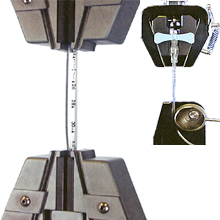
Plastic extruded medical tubing is an essential health care product for the delivery of blood, nutrients and gases to the patient, and for the execution of minimally invasive surgical procedures. The tubes, for example catheters, may also be connected to other medical apparatus such as Luer devices, butterfly valves and pipe junctions. A manufacturer of these products must meet strict regulatory compliance in conjunction with optimising the functional design - for efficiency plus patient comfort and safety - while also meeting production costs. An in-house quality testing regime should consider the in-service forces exerted on the individual components and the complete system of which the tubing will be a part. The tubing itself can be tested for tensile strength and elongation behaviour with a force test stand and a selection of appropriate grips and fixtures pertinent to the product’s performance requirements in situ. A computer-controlled system is perfect for an OEM’s research and development lab, allowing the collection of results and bespoke test programs applicable to a range of products. The challenges to reduce the wall thickness to minimise trauma and maximise the lumen bore to maintain flow capacity can be met with structured, repeatable quality testing processes.
Mecmesin Systems: MultiTest computer-controlled force test system, 5 kN wedge grips, bollard grips
White Paper: Force Testing Medical Tubing
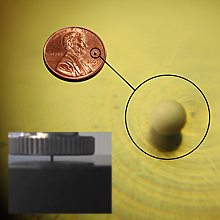
Crush strength is the peak compressive force required to take a sample to its [ultimate] compressive strength at which the onset of failure occurs. A single pellet crush test could be applicable to products such as pharmaceutical tablets (or similarly shaped confectionary), ceramics and industrial catalysts formed of solid material. The implications of failure in these industries is of varying degrees of impact – the industrial catalyst may result in plant shutdown and thus stringent testing is required. The physical shape of the pellet affects the exact test standard method: tablets and spheres being crushed by a different method to extrudates, granular or irregular shaped products. To accurately measure the mechanical properties of a single sphere under load, the use of self-levelling compression plates should be employed. A computer-controlled test stand will enable the first peak load to be captured as the sphere fractures and provision to avoid overloading of the loadcell as the fixture attempts to move beyond this point should be considered. Some examples of the spherical carrier are less than 1mm in diameter and control of the crosshead’s displacement is essential – either physically or by means of the software.
Mecmesin Systems: MultiTest computer-controlled force test system, self-levelling compression plates
Case Study: Alumina Sphere Crush Test

The majority of syringes are single use, disposable and manually operated. Consistency in plunger operation (smooth, and to a correct pressure) is essential, so quality testing requires representative gripping of barrel and plunger, and complete repeatability. Glide force testing can include both filled and empty syringes.
Mecmesin designs custom fittings for syringes of all styles and sizes to ensure a secure grip of both parts without distortion and correctly aligned. For filled syringes, these include fluid collection. Testing becomes both quick and repeatable.

Bard Ltd services its biopsy injector units, which are driven by a powerful spring, primed and triggered by finger pressure. To verify spring strength in units returned for servicing, they must be held in such a way that the trigger can be compressed as in use by hand.
Mecmesin devised a custom fixture featuring a quick clamp and stirrup pull bracket. Placing units for programmed testing is quick, easy and reliable, increasing throughput and ensuring complete repeatability.
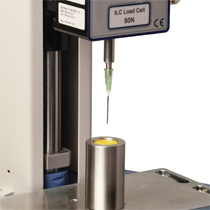
International standards (ASTM F2132, BS 7320) specify the puncture resistance of medical sharps containers. By using real sharps on samples taken from containers, on a programmable universal test stand, repeatable and reliable testing is possible.
Mecmesin designed and provided a Luer hub fitting extension to attach hypodermic needles of various designs to a loadcell, and a tubular sample holder to allow undistorted full penetration of the container wall sample.
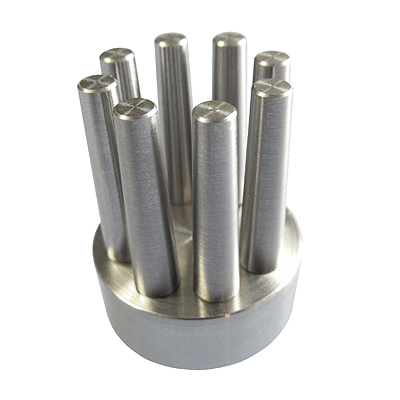

Our client was testing the release torque of 20 mm long plastic catheter caps with irregular features to aid finger gripping. The test is performed by hand with a digital torque sensor, but achieving maximum grip and quick insertion required customisation.
Mecmesin designed a multi-finger mandrel to ensure maximum contact and exact axial alignment. This improved the accuracy of the test through repeatability and cost savings through efficiency in use.
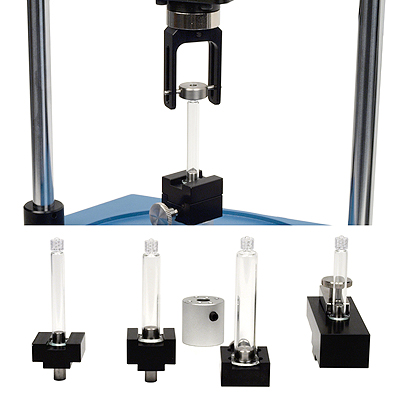

Our client manufactures glass syringes with compression-fit polycarbonate Luer lock adapters. Quality testing requires measurement of the torque required to rotate the adapter, to ensure it cannot come away under normal use of the Luer connection. The syringes come in various sizes, so a flexible range of grips was required.
Mecmesin met their needs with customised grips to hold the glass syringe barrel, and to grip the Luer adapter to turn it, with perfect axial alignment.

Pull-off tests require careful support of the separating parts to avoid distortions affecting the connection, or breakage due to grips. Several of our clients have needed to test the pull-away force of flexible intravenous tubing from connectors.
Mecmesin has designed fixtures to support the connectors in axial alignment with the gripped tube, for fully repeatable testing and rapid positioning of samples. A simple and cost-saving solution to a common, but specific, test situation.
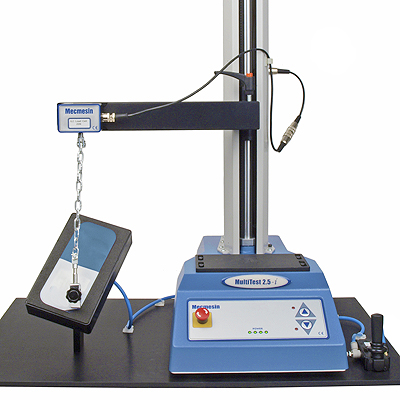

Our client needed to test the peel quality of film lids on semi-rigid pre-filled syringe packs. Inconsistent peeling can result in accidental content spillage, so the force required at a standardised 135 degrees must be measured for a complete opening action. Holding semi-rigid packaging so that it does not deform, requires a custom application for each pack design.
Mecmesin designed and manufactured a vacuum holder for an exact fit to the pack, positioned at the required angle under an extended tensile test arm. The lid was then peeled back with a grip on a flexible chain link. An added advantage of vacuum fixturing is the speed and accuracy of sample changing for maximum throughput and efficiency.

Luer lock test standards frequently involve the application of a simultaneous and prescribed axial force. Our client required fastening and removal torque of caps from from syringes without this. Precision measurement of the torque to fasten and remove the cap needed a simple custom solution.
Two parts, to grip the syringe base and to engage the Luer lock cap, were designed by Mecmesin, and allowed rapid exchange of samples for accurate and repeatable testing at maximum efficiency.
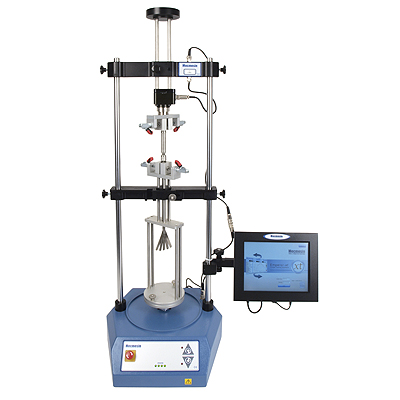

Endoscopic and laparoscopic surgical instruments are operated by axial and rotating adjustments in the handle, to perform precision movement in the head. One manufacturer asked us to provide test fixturing for the operating torque of a laparoscopic instrument in two controls, to splay and to flex the head.
Mecmesic adapted one of its Vortex-xt torque testers by extending its column height to accommodate the instrument length. By fixturing around the length, and gripping the twist controls in the handle, each manipulation could be independently tested for required torque to turn, and smoothness of operation.
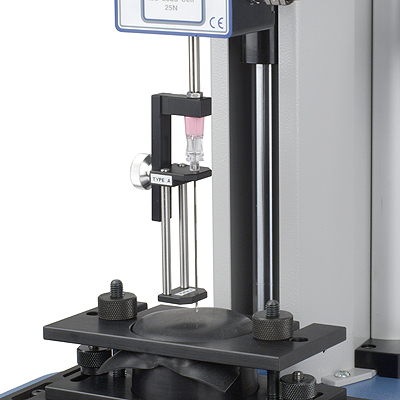

Hypodermic needles can require comparative sharpness testing using synthetic skin, or for the purposes of syringe filling, penetration of closure elastomers such as silicone or neoprene. To do so conveniently, a membrane of uniform thickness elastomer, held under constant tension, can be repositioned for repeat penetration.
For a number of clients, Mecmesin has designed and manufactured custom fixtures for holding hypodermic needle assemblies, and for stretching elastomer sheeting over an aperture for penetration testing. Sharpness is not an absolute value, but the force required to penetrate a vial closure must be consistent, and different point bevels will yield different values. Importantly, during the test, the needle must not flex and the angle of presentation be precise.
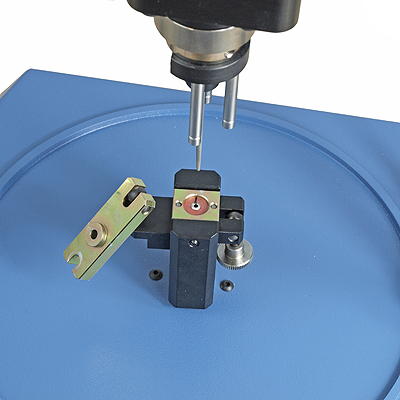
A global supplier of medical equipment manufactures small dental abrasive disks. They needed to test the integrity of the riveted hub, for the torque at which it could begin to rotate in the disk. Clamping the abrasive disk whilst applying torque to the very small hub presented a particular challenge.
Mecmesin devised and supplied a custom fixture for rapid quality batch testing of different sizes of disk on a programmed Mecmesin Vortex torque tester. A clamp secured the outer disk, and a conical probe engaged the hub by friction. By rotating each test sample 90 degrees in one direction then 180 degree in the other, marked samples would clearly show rotation of the hub against the abrasive part.
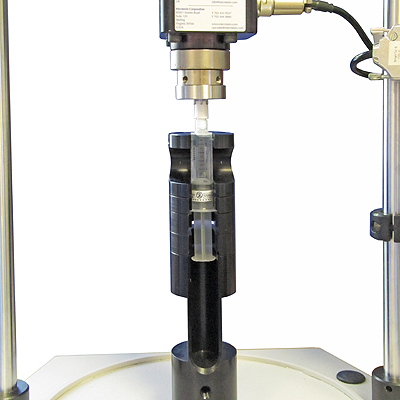

Our client provides prefilled syringes, closed with Luer-lock caps. The release torque of these is quality controlled for consistency, requiring precise measurement and total repeatability for any syringe tested. For efficiency of throughput, the fixture was requested to be single-handed operation and for syringes of different sizes.
At Mecmesin we devised a simple but precise drop-on mandrel for the cap, and an open-sided column to receive the syringe, with flanges for different lengths. Mounted on a Vortex-i torque tester, this povided a rapid and efficient throughput system for quality assessment.
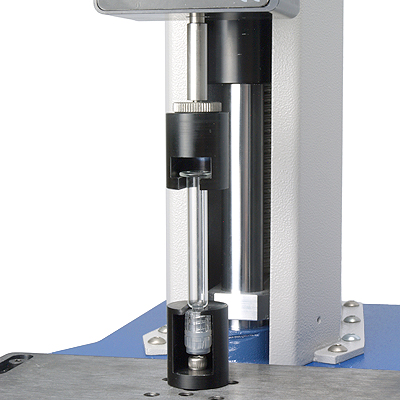

Polycarbonate Luer locks are push-fitted to glass syringe nozzles with a friction fit. Quality assurance demands that they cannot come free under normal use. They can also be tested for removal torque, but our client wanted a direct pull-off test. This required custom grips for both the glass syringe and the plastic lock so that the one would not break and other not deform.
Mecmesin designed and supplied the fixture pair, allowing rapid placement of samples for efficient throughput. The test became a simple, reliable and repeatable exercise.
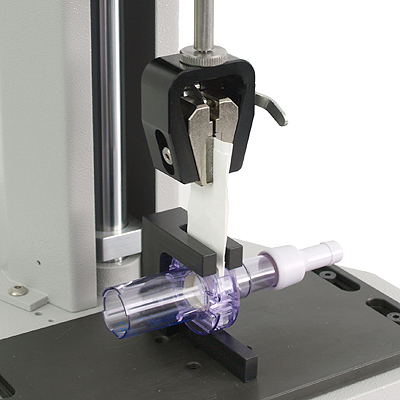

A manufacturer of filtration products needed to test the extraction force of a respiratory filter from an inline holder. A standard wedge grip could pull the filter, but the inline unit needed to be correctly aligned each time for the test.
Mecmesin designed a fixture profiled to the plastic holder, allowing rapid sample insertion and setup for an accurate and repeatable test.
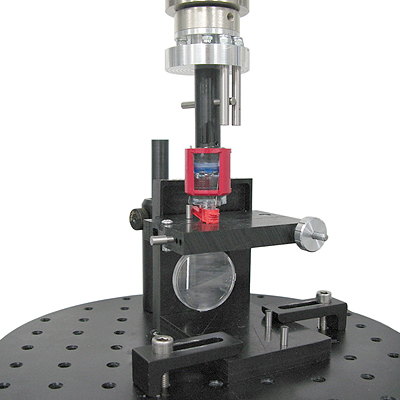

Adlens manufacture adaptive spectacle lenses, where the optical power is adjusted by a side dial which is then removed. Among other tests, they needed to measure the running torque and rotation to destruction of the dials, to test for smooth running and consistency. An essential element in such low-torque testing is concentric alignment for detection of imperfections.
A Vortex-i torque tester with Emperor software was fitted with a custom fixture to support the lens piece, whilst a custom-moulded mandrel engaged the adjustment dial. The fixture pair enabled adjustment for accurate alignment, repeatable testing and detailed examination of the dial rotation quality.
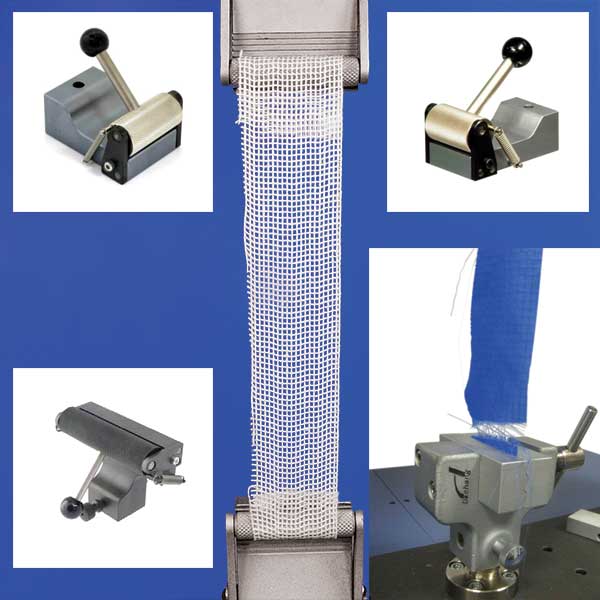

Medical textiles reach their end user in both yarn or fabric forms, necessitating a specific test in order to evaluate the quality of the product for its intended purpose. The materials themselves must meet stringent requirements over and above their physical properties such and strength and flexibility—relating to hygiene and resistance to infection, or the need to be non-reactive in the case of implantable textiles. Individual yarns (for example suture thread) should be tested for ultimate tensile strength, to minimise uncontrolled breakage, but facilitate breakage or cutting when required by the surgeon. Motorised test stands fitted with roller or bollard grips ensure reliable measurement of truly representative sample breakage, away from fixture clamping. Clothing and other protective garments must be evaluated for tear, peel and puncture/penetration resistance as well as ultimate strength and elongation properties. Mecmesin’s universal testers and dedicated peel and tear test systems can accurately measure the performance of medical fabrics to international standards against Delft, tongue, single rip (trouser), trapezoidal and Graves tear procedures. Computer controlled systems enable specific in-house tests to also be performed. Some fabrics may also require a degree of penetration resistance which is easily evaluated by our UTM systems. Patient dressings must be flexible enough to cover any part of the body and also protect and support many types of injury, thus the measurement of elongation and ultimate tensile strength enables the manufacturer to quantify the performance of the textile completely.

The helical torsion spring comes in a wide range of designs and varying sizes to cover almost every engineering application. Despite being termed ‘torsion’, the spring itself is subjected to a bending stress when the ends rotate about its central axis, driven by the components attached to either arm. The elements which are required to rotate in service depend upon the spring’s stiffness rating in order to be fit for purpose and also exhibit the correct level of resistance for ease of operation and quality feel. The smallest examples, used in precision applications, need to employ a test system which can not only ensure that the spring’s axis remains aligned to within tight tolerances but that can accurately measure the resulting very light torque values. In these implementations, the frictional forces experienced by the coils may have significance. A spring design with pitch between the coils, rather than close-wound, will counter this issue and allow for even lighter torque to turn efforts, increasing the need for a torque test system capable of measuring these values. Exacting alignment of the fixture (hence spring) and torque cell axes for concentricity should be a capability of the test stand to guarantee the most accurate data.
Mecmesin Systems: Vortex computer-controlled torque testers, Emperor™ (Torque)
 Luer fitting slip, running torque and force testing
Luer fitting slip, running torque and force testingLuer lock and Luer slip fittings commonly attach hypodermic needle hubs to syringes and other fluid transfer medical devices or laboratory instruments to provide leak-free connections via a 6 percent taper at the joint. Both the threaded and friction types must require a high enough torque not to disassemble in operation and still maintain the hermetic seal, whilst still allowing easy and quick engagement/disengagement of the connected system. Breakaway and running torque tests are the means by which these performance criteria are evaluated. The quality assurance testing of mass-produced medical Luer slip and lock fittings demands precise control of concentricity at extreme low torques which is facilitated by the use of specific fixtures for accuracy and repeatability – industry standards often stipulating that the sample be assembled to a particular precision steel reference fitting. The Ease of Assembly test requires the addition of an axial force in conjunction with the rotational force, and a testing system which allows the precise application of this force is essential. The Unscrewing Torque test ensures that the Luer connection can be unscrewed with minimum trauma to the patient.
Mecmesin Systems: Helixa precision torque test systems
 Dosage pen dosage dial torque testing
Dosage pen dosage dial torque testingThe medical industry demands that the administration of dosage requires the correct dosage to be injected for the individual patient. The rotational dial of an dosage pen’s dosage regulator must turn easily but positively enough to allow the correct number of dosage units to be accurately delivered from the disposable multiple use cartridge. In order to test the light breakaway and running torque values required to operate the dosage dial, it is essential to eliminate friction and position the sample with absolute concentricity. A torque tester that features a counterbalance to negate the axial force of the grip and torque cell in addition to precise adjustability of the alignment between the torque cell and the spindle is required. Fixturing for the sample should also ensure that it is maintained in an upright position.
Mecmesin Systems: Helixa precision torque test systems
 Biopsy needle injector gun spring strength
Biopsy needle injector gun spring strengthA biopsy stylet and cannula injector gun is a medical appliance for quickly and reliably extracting a tissue biopsy sample. A prime component in this hand-held device is a powerful spring, which is compressed by a single finger trigger action. The tolerances for the compressive spring rate are very specific - low enough to allow a user to operate the mechanism and cock the gun, yet high enough to perform a full and effective insertion and withdrawal of the needle. Stringent compressive strength testing standards require multiple tests on each injector gun to ensure repeatability and reproducibility at the quality control stage of production or refurbishment. A bespoke fixture to simulate the finger and apply the trigger pressure, whilst holding the medical device securely may be needed.
Mecmesin Systems: MultiTest motorised test system
Case Study: Biopsy injector spring strength
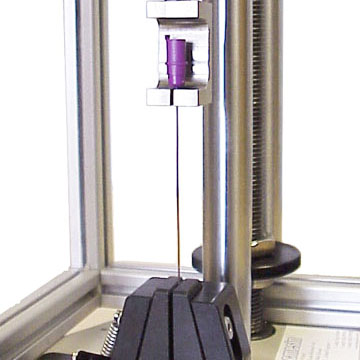 Needle and lancet pull-out testing
Needle and lancet pull-out testingSurgical needles and lancets may be located in their hub or ferrule by a variety of methods, including bonding, moulding, welding, mechanical interlocking, and sealing. The retention, or pull-off strength of the assembly method must be sufficiently high that the peak frictional force during usage does not cause disassembly or seal failure resulting in the needle remaining in the patient. To test the pull-off/pull-out performance, the test system is normally fitted with a suitable mounting block, to support the hub in such a way as to leave the needle tip exposed vertically. In the case of smaller needles and lancets, a lever-operated pin vice may be used to grasp the tip, and for larger gauge needles, a wedge grip may be required to hold the sample. An axial tensile load is applied at a constant rate, until the needle is completely dislodged from the hub. For safety considerations, the test system should be contained in a protective enclosure to provide protection from the fracture and breakage of sharp objects.
Mecmesin Systems: MultiTest motorised test system, digital force gauges, manual test stands
Case Studies: Lancet needle retention test, needle pull-out test
White Paper: An Examination Of Needle And Syringe Force Testing
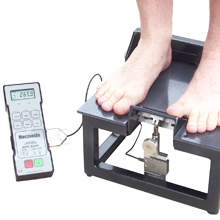 Physiological measurement of joint exertion force
Physiological measurement of joint exertion forceMedical and veterinary facilities can utilise force testing equipment to evaluate the capabilities of human (or animal) subjects for any number of research projects. One purpose may be for the collection of data as input to the design of occupational health and safety products or equipment. In the specific example of the range of joint strength in patients' big toe (the metatarsophalangeal joint), the angle of the toe may also be significant. A bespoke testing platform incorporating an intelligent loadcell, would be required to allow the positioning of the foot consistently and hold the toe at measurable, variable angles. A portable digital gauge could be easily employed to capture the data from individual patients over time, and the compressive strength results analysed and used for research or educational purposes.
Mecmesin Systems: Advanced Force Gauge, S-Beam loadcells
Case Study: Physiological Measurement of Joint Strength
 Surgical suture thread tensile strength and elongation at break
Surgical suture thread tensile strength and elongation at breakIn the biomedical engineering industry, the reliable performance of surgical sutures is vital to wound healing and hence the wellbeing and recovery of the patient. Differences in gauge and material constructs (e.g. hybrid metal wire/polymer yarn, or other specialist textiles) are required for different purposes, with functional requirements such as being absorbable/non-absorbable or antimicrobial also affecting the physical qualities of the thread. The measurement of the strand’s elongation at break and the force required to snap the thread provides an objective and comparable method of evaluating these advances in medical technology. To successfully test the ultimate tensile strength of the fibre, it must be ensured that the grips securely hold the sample, whilst being light enough to allow the use of a loadcell with the optimum accuracy for the force range. Any slippage will compromise the precise measurement of the elongation, which may be a critical parameter in the back-to-back comparison of alternative constructs. The use of a computer-controlled force test stand with specific fixtures allows healthcare product OEMs to optimise the design of medical textiles for effective healing and minimal cosmetic impact.
Mecmesin Systems: MultiTest computer-controlled test system

Closure torque testing involves a range of tests for events designed into screw caps, lids and unthreaded stoppers. It can include a measure of the turning force required to initiate twisting, possibly to overcome safety features (e.g. CRC Types I and II) and tamper resistance features, and also to secure the closure. Other rotational systems, for example bearings, also benefit from the evaluation of the required torque to turn—both breakaway and running torque. Accurate measurement of the torque characteristics of these systems requires alignment of the rotational components with the grips and fixtures of the testing equipment. In the case of large or irregularly shaped products, custom designed fixtures may be needed to assure concentricity of the closure with the crosshead, and permit adequate clearance throughout the complete angle of rotation performed in the test.
Mecmesin Systems: Vortex torque testing systems with customised testing fixture design